People are burning cell masts and ignoring the law by protesting the construction of a 5G network.
People are becoming increasingly concerned that the new networks will make them sick. I am convinced that you also have doubts and you do not know who to believe. I will reassure you by inviting you to listen to a conversation with a specialist on EMF impact.
For now, however, I invite you to read about the revolution, which will result in some of these fears and problems being resolved.
You probably know the saying that “Every revolution begins with a spark”?
The spark, a new law ordered by the European Union, will make mobile networks undergo a real change towards modern 5G networks.
At the end of 2020, a real shift towards the development of 5G network coverage with small cells will begin.
Small cells are simply base stations with low radio power transmitted from the antennas and therefore a short range, with a radius of several hundred meters.
The new law, EU regulation – implementing regulation of the European Commission of 30 June 2020
Something has happened that the Small Cell Forum has been working on for several years. (Illustrations in the document come from the document: SCF market, Document 050.10.4)
The European Union Commission has issued a draft of a document describing the implementing regulation. It is a new law that applies to all members of the European Union, including Poland.
Why, in my opinion, this document is the spark that will eventually revolutionize the construction of 5G networks, but also LTE?
How is it that many people do not realize that this small, 7-page law could change the world of mobile operators and infrastructure providers?
Why in my opinion will this law stop the protests and prevent some people from scaring us with 5G networks?
Because this regulation destroys the basic assumptions regarding the construction of cellular networks. The larger and higher the cellular mast, the better the network.
The new law on permits for small cells introduces the possibility of building cellular networks with very good quality. The surprise is that schemat will be based on low-power devices.
Here are the basic provisions of the small cell 5G law regulation:
- Radio equipment of class E2 (2 Watts of EIRP power) and E10 (10 Watts of EIRP power) will not require a radio license to implement them (standard EN62232: 2017).
- Within 2 weeks from the moment of installing the devices, the operator must inform the relevant services about their activation.
- The dimensions of the device should correspond to the size of a box with a maximum capacity of 30 liters.
- The applicable standards for radio equipment must be complied with.
- Devices must be integrated into the architecture of the surroundings. Installation must consider the aesthetics of our landscape and not be conspicuous.
- The devices must be hung above a height of 2.2 m. In the case of closed or roofed spaces, the ceiling must be above 4 meters.
- The regulation applies to all members of the European Union.
- The regulation comes into force on December 21, 2020.
Why is the law supposed to change something in the quality of the network? Why do I think this is such an important change?
The law alone cannot change anything, but it can affect it
The aforementioned regulation changes a lot.
For base stations below 10 watts, you don’t have to go through a long, complicated and tedious procedure with loads of papers and permits.
No need to obtain a permit to turn on a radio device is a huge simplification and acceleration in the development of coverage by cellular networks.
But is it just about ensuring network coverage, that is, coverage?
Many small base stations are much more than one large radio station
In the current model of network construction, operators prefer to build the base station on tall buildings or on towers for several reasons.
- The higher the antennas are, the greater the range, which means that from a distance from our phones, such a station is able to handle them.
- Putting a larger tower in the field is a lower cost than building a few smaller towers. For example, to replace a 60-meter tower, you need to put three to four 20-meter high towers.
- The tower can be rented to other operators. The partner helps pay off the construction costs.
- You can cover a huge area faster with taller towers.
There are many technical and legal barriers, which is why the operator cannot freely place additional base stations in cities and densely populated places.
In places where many people live, problems related to:
- Network coverage, affecting the quality of voice calls.
- The quality of the network during peak traffic hours, i.e. the speed of the Internet.
- Increasingly greater consumption of electricity due to the increase in the number of devices in existing locations.
- Protests due to antenna installations scaring their view.
Small cells and new law, or technological “Small is beautiful”
Experts, trying to solve the problem of high base stations, concluded that there is no better solution in cities than building many small, low-power base stations at lower altitudes.
The implementation of a dense network of small cells will solve most of the problems that I mentioned earlier.
It will provide capacity, quality, low power consumption, and less radiation from the antennas.
Thanks to the small cells, there is no need to place huge base stations on the roofs. The operator can use low-power devices that are integrated into the environment.
Maybe thanks to this solution there will be fewer people feeling threatened and thus fewer protests.
It seems that the new law offers technological Win-Win opportunities for everyone.
However, I will make a reservation that you cannot completely stop building large towers, because communication is also needed in an unpopulated area. In this situation, the operator will use the existing towers when building a 5G network.
How will the new law affect the 5G network building model?
The operator, in most cases, does not own the place where the base station stands. The operator is leasing this place.
In the case of building a huge 5G cellular network based on small cells, the model will be the same.
However, the form of searching for a location will change. For the construction of a roof station in Warsaw, approximately 500-800 locations are needed. If we start expanding the network at a level of 2-4 meters using 10 Watt devices, there will be thousands of potential sites.
In order to gain multiple locations, the operator will then start looking for strategic partners who have a huge number of buildings, billboards, poles, lanterns, etc.
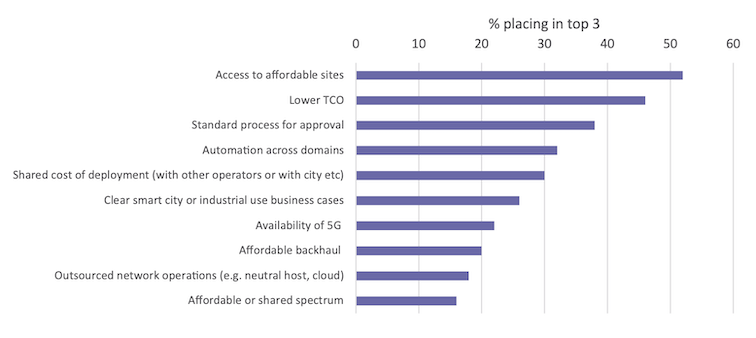
This is an opportunity not only for network operators but also for owners of various types of buildings with a height of several meters.
It is easier, cheaper, and faster to sign a collective agreement than to negotiate individual agreements.
Will the new law affect the market of telecommunications infrastructure providers?
The big five (Ericsson, Huawei, Nokia, ZTE, Samsung) have so far not supported the small cell model.
They are sticking to the model based on expensive, large base stations, bringing them more profit.
If you are interested in what is happening in the world of cellular infrastructure providers, you’ve probably heard about Open Ran, TIP, or the aforementioned Small Cell Forum.
A common feature of these organizations is the promotion of radio solutions based on software-controlled radio devices.
The Small Cell Regulation is therefore “water to the mill” for new suppliers as their potential for creating and producing 10 Watt devices is theoretically unlimited. They can:
- Mass production of CHEAP, efficient, simple radio devices.
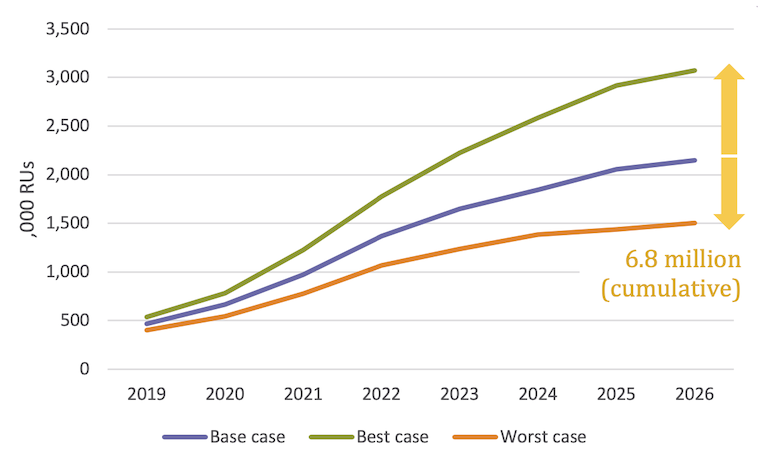
- Develop more and more intelligent software drivers installed on EDGE/MEC servers. Such software helps to improve the quality of the network LOCALLY depending on specific conditions. For example, the MEC server can control the resources of all small cells in a large housing estate, ensuring good quality.
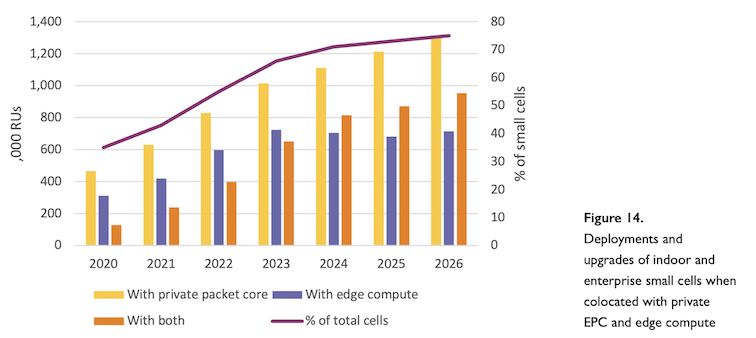
The great suppliers are stuck in their own snares. Expensive licenses and solutions do not allow them to scale their offer at a lower level, because it is not profitable for suppliers.
Why has it not happened so far, despite similar solutions?
The current players in the mobile market probably do not really believe that the revolution described here could affect their present world because:
- Operators are stuck with the big turret model.
- Suppliers are stuck in the oligopoly model and very high prices. It is better to sell the operator expensive devices and licenses for the macro network.
- Market regulators are stuck in the model of charging crazy sums for national frequencies.
- The market and operators have come to believe that they should provide FTTH fiber networks rather than look at a different network construction model. Without introducing any innovations, they are based on proven solutions.
The current value chain for mobile operators has grown old and lost the opportunity to grow. Although 5G is, as always, a real revolution, today’s players are afraid of what may happen, i.e. the emergence of small competing private networks.
The forum’s small goal did a great job of persuading the European Union to introduce the regulation. It seems the wheel is gaining momentum.
On December 21, 2020, the regulation enters into force, on exactly that day everything will start to change.
What makes us happy is the fact that in the new version of the )telecommunications law, the so-called European Electronic Communications Code (EECC) this regulation will be taken into account. Currently, EECC is also being established in Poland. We keep our fingers crossed for the success of the new law.
At the end
Hope that after reading the article you will share my enthusiasm for implementing a 5G network based on small cells.
The road to convincing operators, customers or suppliers is still long, but it can change the status quo like never before.
In my opinion, this regulation is much more important for Poland than the change in PEM limits, which took place in December 2019. The change of PEM was to enable operators to build a 5G network. Yes, but in the model of base stations on roofs and towers.
However, along with the change in PEM limits, the restrictions on the qualification of radio installations have not been lifted, which still prevents them from successfully building the network.
What do you think of the new small cell law? Do you think changing the way mobile networks are built can end the protests? Leave your comment under the article.
