At the beginning of the year, a quick entry, the hero of which is a 5G mobile phone.
I will convince you that it is not so obvious what 5G mobile phone to choose. Due to fact that there are many technical aspects regarding this device, it can be difficult.
It just so happens that we can select 5G mobile phone from a group of more than 500 models. This was announced by the GSA (Global mobile Suppliers Association) monitoring the 5G market.
So, let’s look at what kind of devices they are, what they are used for and what markets they are designed for.
Why does the issue of markets and more specifically continents matter? Because not every country and continent use the same radio frequencies.
What radio bands does a 5G mobile phone use?
The worldwide radio bands for 5G are two very wide ranges.

Sub-6
The first, called FR1, covers frequencies from 410 Mhz to 7125 MHz. FR1 includes all cellular bands used to build 2G, 3G and 4G networks. However it covvers also new frequencies like 3.4-3.8 GHz. All the bands are called Sub-6 range.
mmWave
The second set of FR2 bands are high-frequency bands, colloquially referred to as mmWave bands. FR2 covers frequencies from 24.25 GHz to 52.60 GHz.
In some countries, such as the US and Canada, additional frequencies are used in the 57 GHz – 95 GHz range.
Let’s remember these two names (Sub-6 and mmWave), because these are the basic bands for 5G mobile phones. You will hear about them again in the coming years.
5G band naming
Different band ranges have different names and correspond to different frequencies.
The bands used by 4G networks start with the letter “b”.
Bands used for 5G networks begin with the letter “n”. Band numbers are indicated by one, two, or three digits. Unfortunately, subsequent numbers do not indicate an increasing frequency. One and two-digit names refer to the Sub-6 bands and the three digital mmWave bands.
Overlap of radio bands
Unfortunately, some inaccuracies are hidden in the numbering of the bands. This includes sub-6 and mmWave bands.
- Pieces of individual bands with the same number can mean different frequencies. For example, the US uses the n258 (mmWave) bands at 24 GHz and 28 GHz. In Europe the same n258 band name refers to the 26 GHz.
- Individual strands can overlap with a piece of band. For example, n257 and n258.
- In addition, smaller bands can be separated within a larger band range. As example, n261 falls within the n257 band range.
These nuances are extremely important when choosing a 5G mobile phone. For example, the aforementioned n258 band is supported by the iPhone12, but only for parts of the US band not for Europe.
Unfortunately, this unfortunate issue of naming a wide band with one and the same name is cumbersome for experts and can mislead customers. Antenna and base station suppliers must take this into account when purchasing network construction equipment.
An additional confusion is the lack of dependence of the band name on the frequency. The same frequency e.g. 2600 MHz, but used with different technical parameters, can be used on different bands. In this case, two bands are defined for the 2600 MHz frequency: n7 and n38. The first used for FDD technology and the second for TDD.
More and more suppliers of 5G RRU radio transmitters are on the market. Open RAN providers from different parts of the world have a different understanding of the core bands.
Shall you panic about selection of your 5G mobile phone?
Before you reach for pain pills, I want to calm you down. A 5G mobile phone purchased from an official store or operator meets the relevant criteria. However, if you are tempted by a super promotion you dare to buy your phone yourself on Aliexpress without the advice of an expert, I advise you to buy these pain pills first. Problems you have guaranteed.
Well, enough of this theory, just scaring, let’s move on to what’s more interesting.
Are all mobile phones commercial?
In November 2020, a list of 500+ 5G devices was announced, but not all of them are manufactured devices, some are products just announced. The commercial mobile phone is represented by less than 300 models.
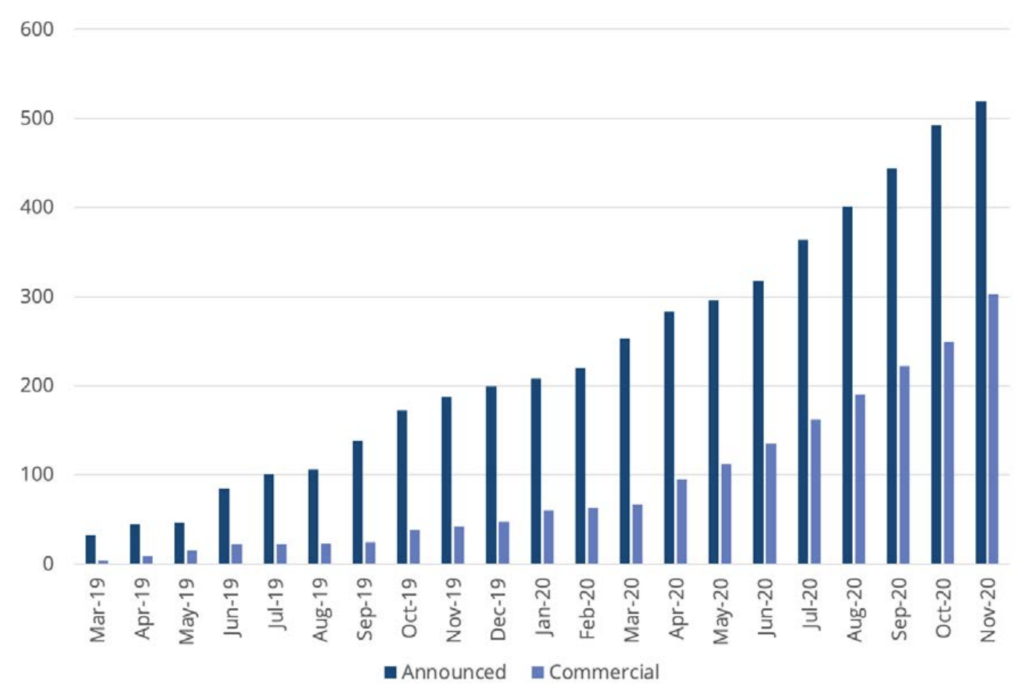
Nevertheless, success is.
Why do I call it a success, even though the numbers are significantly different?
Because of the reachability of 5G mobile phones, before 5G networks were created.
In the past, working with mobile operators, I often had the dilemma of introducing new technology when there were no terminals supporting it on the market.
For 5G, the opposite is true. Yes, it should look like.
The curve of supported 5G mobile phones is growing, so let’s look at the details, because the devil is always in the details.
Are all 5G devices mobile phones?
Mobile devices are not just mobile phones.
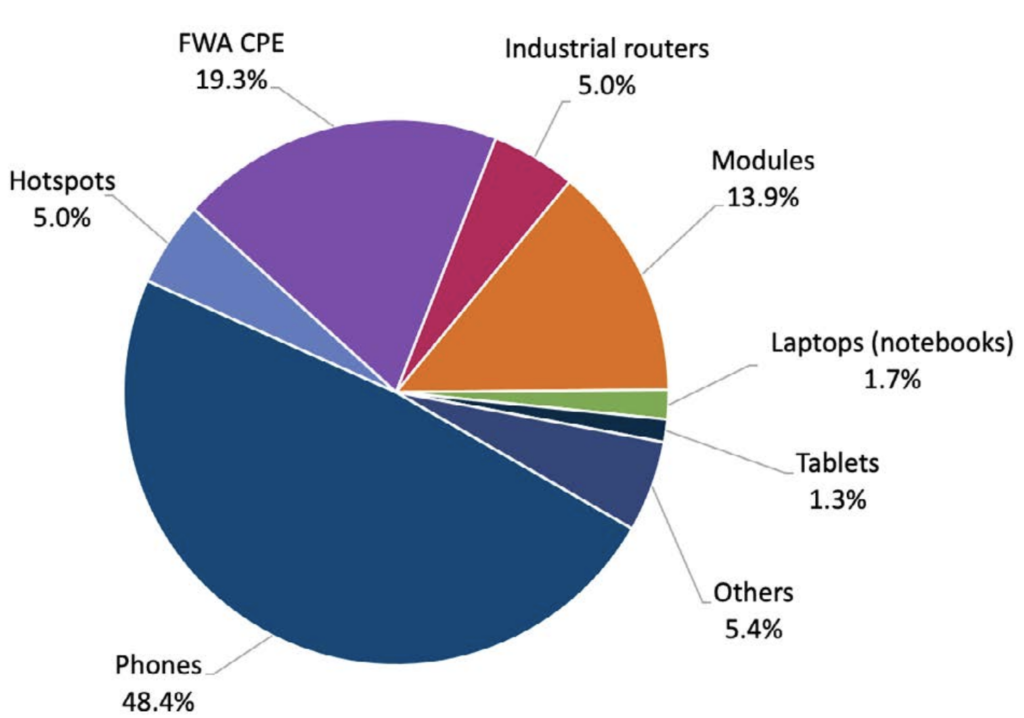
Manufacturers’ statistics show the following uses and their market share:
- 48.4% are mobile phones, which is what we carry in handbags and pockets.
- 19.3% are Fixed Wireless Access Customer Premises Equipment (FWA CPE). The name is terribly long, but the device is adored by customers living in homes. These devices are nothing more than modems for 5G Internet access mounted on roofs or set on the windowsill. As you can see, it’s a big category, a fifth of the whole range of devices.
- 13.9% is a category of 5G modules. Modules are very small electronic components for installation in other devices. These can be beverage sales machines, car position tracking devices, energy meters, water etc. It’s a big category and it’s no surprise. Have you heard of the development of the IoT (Internet of Things) market? It is the most important industry to win the control equipment market.
- I’ll mention the summed-up categories of 5G devices mounted on laptops (1.7%) tablets (1.3%). Practice shows that it makes no sense to mount dedicated 5G modems on portable devices other than mobile phones. After all, WiFi access is enough.
And which bands are manufacturers preparing their new 5G devices for?
Want to learn more about the 5G bands used on mobile phones?
At the beginning of the article, I showed a very wide spectrum of frequencies provided for 5G networks.
From detailed statistics, however, you can see that the vast majority of devices support Sub-6 bands. This does not surprise me, because the basic 5G band is the 3.4-3.8 GHz band range from the Sub-6 range.
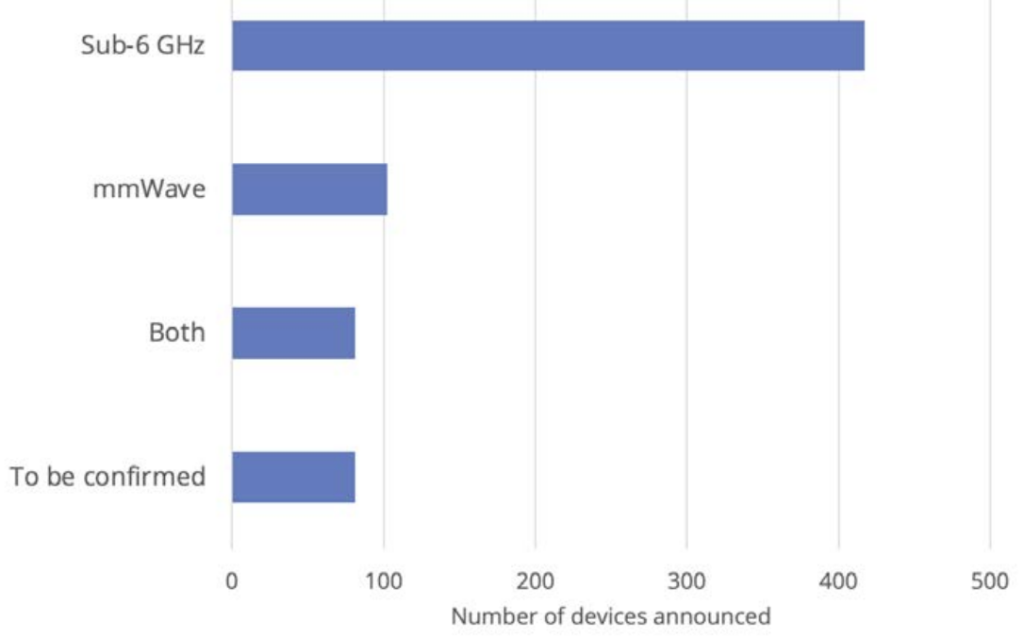
One fifth are devices adapted for receiving mmWave bands. This is the basic band used in FWA CPE devices, on the US market. These bands have been present there for several years now. The REGULATORY AUTHORITY in the USA has allocated mmWave bands for commercial use to individual customers much earlier than the European authorities. In the past, mmWave bands were mainly used in Europe to operate transmission devices, so-called microwave links.
What surprised me most, however, is the fact that less than 20% of the terminal types are prepared for the parallel reception of the FR1 and FR2 bands. I mentioned this phenomenon on the occasion of an article about the iPhone 12.
The range of the n258 band is wide and only part of it coincides with the European or Asian range. In the US, the n258 band is already used and this is supported by current 5G mobile phones. Europe and Asia are just getting ready to select and allocate licenses for each mmWave band.
Who can impact 5G mobile phone features?
It is the manufacturer of the mobile phone that decides what bands will be supported by the phone, and this depends on economic factors.
The mobile phone is supposed to be as cheap as possible (looking from the perspective of the manufacturer not the customer, it’s so by the way), it has to have a large display and the battery is supposed to last a long time.
The most expensive part of the mobile device is the radio processor (chipset). It is responsible for the operation of various radio bands. More bands operated simultaneously means more power consumption, larger size and higher mobile phone price.
Is it supposed to be cheap? It’s cheap.
I would like to see with you what exactly the band numbers are supported by mobile phones.
We already know that sub-6 terminals dominate. What exactly the frequencies are most popular in these phones is of great importance to mobile operators.
What band ranges are the most popular in 5G mobile phones?
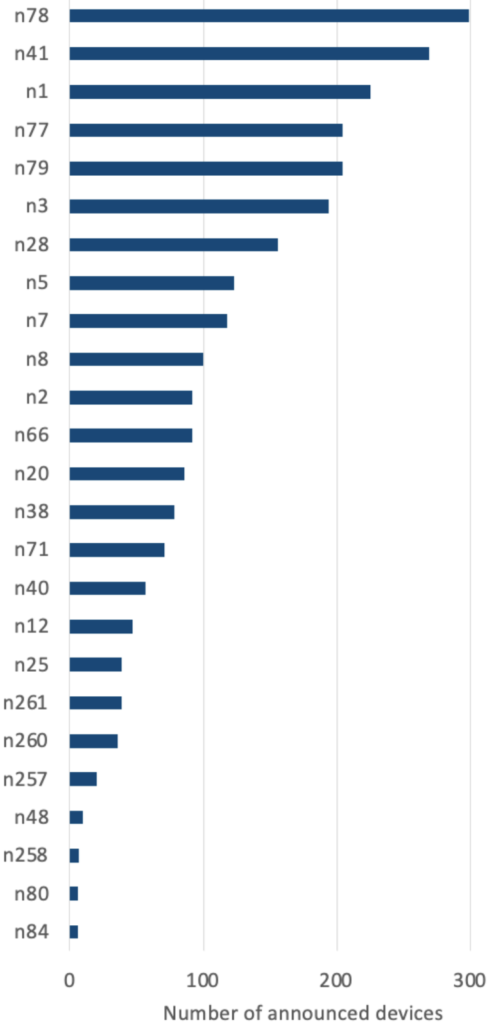
Let’s examine in detail the statistics of the individual bands:
- In the first place dominates n78, that is 3.4-3.8 GHz, as I mentioned this most important 5G band. The quantity is therefore not surprising.
- In second place is the n41 band, at a frequency of 2500 MHz. This is a fairly specific frequency, used for quite a long time by the mobile operator Sprint in the USA.
- The third place is occupied by the n1 band at 2100 MHz. This band is used by mobile operators to support 3G/UMTS, 4G/LTE and more recently and 5G networks with support of DSS technology. Some European operators, like in Poland, have launched the current 5G network prototypes on this band. In this case, this is an advantage for the operator, because it can implement a 5G network on the existing band. For the customer, unfortunately, this is a disadvantage. Part of the 2100 MHz range is designed for 5G networks at the expense of 4G Internet speeds and the need to disable 3G networks locally.
- The fourth band is the n77 (3.3-4.2 GHz) ranges slightly wider than the n78 (3.3-3.8 GHz) and n79 (4.4-5.0 GHz) ranges. The n79 band is used in China and Japan.
- It is probably worth mentioning the n3 band (1800 MHz). In Europe, it is used en masse by operators for 2G, 3G and 4G networks. As you can see from this statistic, you will expect operators to use it to deliver 5G networks at the expense of older technologies. About disabling old bands for 4G and 5G networks I wrote in an article about VOLTE roaming.
What bandwidth is most important for a 5G mobile phone?
In conclusion, it is worth noting that customers buying a 5G mobile phone can always use the 3.4-3.8 GHz band.
Well, in some countries, before the development of 5G networks happen, we need to use “almost 5G network” in the n1 band.
What does a 5G chip mean for a 5G mobile phone manufacturer?
I mentioned earlier the issue of the radio chip used by mobile phone manufacturers. It turns out that not every phone manufacturer can afford to produce their own chips. Designing and manufacturing a chip is a very expensive and complicated process. For this reason, most manufacturers, including flagships, buy radio chips from partners.
It’s time to meet the manufacturers of key components of your mobile phone.
Who makes radio chips for 5G mobile phones?
The number of chip manufacturers is modest, but their profits astronomical. Until recently, the market was dominated by two three producers, but the situation is changing from quarter to quarter.
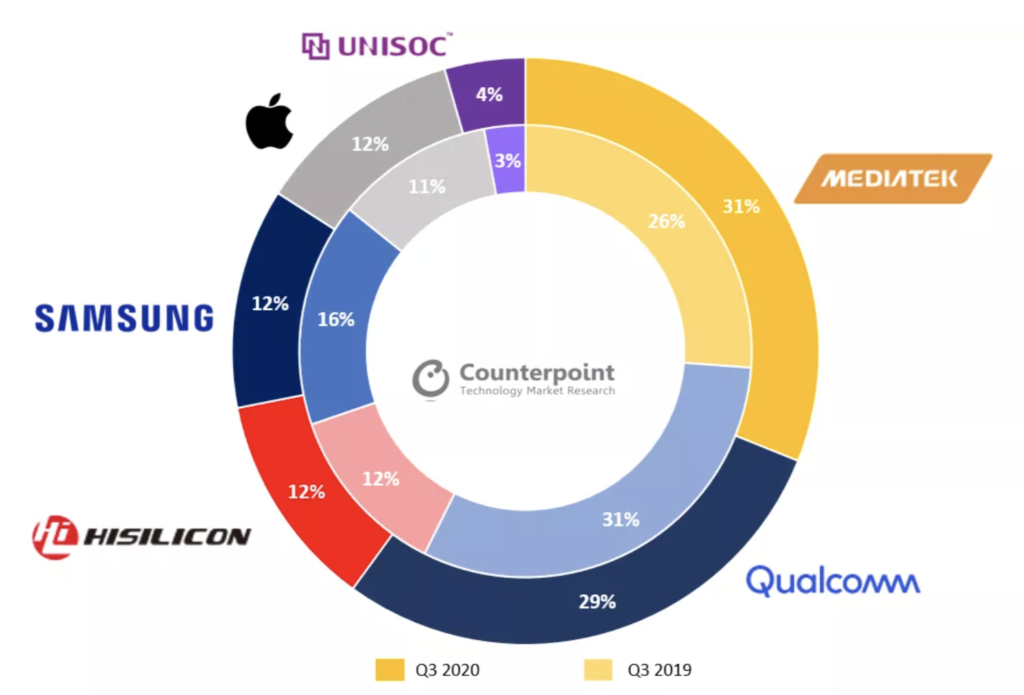
In recent months, there has been a change of leader among mobile chip manufacturers. Qualcomm in the US was the undisputed leader. MediaTek from Taiwan has been trampling on its heels for some time. They were so trampled, trampled, that she took first place in the third quarter of 2020.
How did it happen that until recently an unknown company MediaTek achieved an increase in sales and market share? Such great success is due to cooperation with Chinese phone manufacturers, putting on sale a huge amount of relatively cheap devices.
We are talking about companies like Xiaomi in Europe (3 times the share of MediaTek chips in Xiaomi mobile phones increased), Oppo or Realme.
As an example, I will give the price of relame’s Realme 7 5G terminal, widely promoted in Europe. In January 2021, this device cost only 180 EUR! By comparison, the cost of producing the iPhone12 alone is about 431USD (with 128 GB of memory). The main factor in the increase in the price of the iPhone12 was the 5G radio chip and OLED display. Compared to the iPhone11, the cost increased by 26%.
MediaTek has focused on a strategy of simple, efficient chips. Of course, these chips do not match those of Qualcomm or Apple.
Qualcomm, under pressure from MediaTek, announced at the end of 2020 the implementation of a simpler version of the radio chip to maintain the market for low-cost mobile phones. The competition is beautiful, isn’t it?
Smaller, equally important manufacturers of 5G chips for mobile phones.
Let’s take a look at what’s going on with samsung’s mobile phone sales leader.
Samsung terminals are mainly using on its own Exynos processors (or just?), however Samsung is losing market share and their biggest rival Apple with the A-family processors, is slowly growing. Apple is sure to start gaining that part of the market with its first 5G terminal with its own A14 chip. iPhone12 is currently one of the better-selling 5G devices.
Before the last manufacturer in the list is HiSilicon, a subsidiary of Huawei. It maintains its position but cannot grow too much due to the ban on the sale of their terminals in the USA or Australia.
The fifth major player is Unisoc from China. The company’s processors are used by manufacturers such as ZTE, Lenovo and many small Chinese companies starting in this industry. Interestingly, even Samsung uses their chips for simpler versions of mobile phones.
Definitely, the 5G chip market is starting to be the domain of Chinese companies, and asian companies are leading the way.
When it comes to 5G chip manufacturers, the future is bright, decidedly Asian. I will just point out that the entire US war, China, began with Broadcom’s attempt to take over Qualcomm, which belongs to Singaporean companies with Chinese ties.
As I mentioned, the processor is uneven processor. What is not a mobile phone with a cheaper radio processor?
What features do cheap 5G mobile phones not have?
What’s different about these processors is the range of functionality.
Basic functionalities differing radio chips:
- Support for 5G SA networks,the next generation of 5G core networks. This is just a growing standard, but crucial for the development of real 5G networks.
- Support for band aggregation up to 100 MHz (TDD and FDD). Cheaper products can’t do that.
- Sub-6 and mmWave band aggregation. Only the best and most expensive like Qualcomm X60 chips can do this.
- Support wider mmWave band because as much as 800 MHz. Cheaper versions support up to 400 MHz.
- No support for mmWave bands. I described this topic above.
- Support for DSS function, used to support 4G and 5G networks on the same band. This is how operators in Poland do it.
The more functionality, the more expensive the chip.
Looking at all this realistically, today the operator must be ready to build a network in the n78 band (3.4-3.8 GHz) and support 5G networks using DSS on the 2100 MHz band.
What mobile phone features will be important for operators in Europe in the future?
Support for 5G SA and mmWave technology at 28GHz?
If I were to decide today to introduce 5G mobile phones, I would choose as necessary the following functions: n78 band, n258 band, 5G SA, DSS at 2100 MHz and 1800 MHz. In the future, I would look for terminals with aggregation of n78 and n258 bands.
Finally, a few more words about mmWave, because this technology has as many advantages as disadvantages.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of mobile phones on millimetre waves (mmWave)?
I will write to you at the end what are the advantages and disadvantages of mmWave bands.
Advantages:
- Operators will have very wide mmWave bands at their disposal. 400 MHz or even 800 MHz. What does this mean? The wider the bandwidth, the higher the internet speed offered by the operator or otherwise has the ability to serve more customers with good quality.
- There is no need to aggregate several bands. The spectrum of mmWave bands is huge, because it reaches up to 2 GHz. This allows the operator to build cheaper base stations.
The biggest drawbacks:
- Very low operating range of such frequency due to the reflection and absorption of waves by obstacles. The customer must be close to the antenna to reach high speed.
- Doubts about the safe use of mmWave waves.
On one hand, we are talking about the support of one band with a wide spectrum of 800 MHz, but on the other hand we are talking about low-range waves. These bands require finding a new generation of technologies and devices to improve the situation. There is something to beat about, because the width of the mmWave bands gives everyone a chance to access a really fast and very roomy Internet.
Manufacturers of mmWave devices are betting on looking for innovative radio technologies that will improve the first of these inconveniences, namely the small range.
Technologies such as active antenna systems and Beam forming antennas are designed to solve this problem.
Do you already know what 5G mobile phone will be yours?
Soon, there will be a lot of 5G mobile phone types. I can safely assume that at the end of 2021, 70-80% of terminals in the operator’s offer will be 5G support devices.
What we should enjoy the most is the fact that the price of devices has been falling. The old good principle of competitiveness has worked. Chinese and Taiwanese companies, effectively competing with American chip and mobile phone manufacturers, are changing price levels.
Do you already know when to buy your 5G mobile phone?
I am convinced that this is a matter of at most the next two years.
So, when choosing a mobile phone in 2021, be sure to choose one that supports 5G networks.
Show operators that we are waiting for new fast and errable networks, better Internet and cool, fabulous mobile phones.
Be the first!
Happy New Year.
For those interested, I will send a link with a list of 5G bands along with all the details.
